About
IoT with backscatter data Transmission is an emerging academic topic. As a course project, we were introduced to backscatter transmission during the Embedded System Master's program. The below introduction to backscatter transmission was taken from the final report that we prepared.
"A longer operational lifetime without human interaction is a main desired feature in wireless sensor-embedded systems. An energy harvesting device or battery-powered device, doing as much computation from the available energy increases the value of that device. Wireless embedded devices spend most of the energy to keep the radio up and running and that decreases the lifetime of that device drastically. Backscatter was introduced as a workaround to this power-hungry communication. The idea is to use the ambient electromagnetic energy to transmit sensor data."
Keywords
IoT, Backscatter, Antenna array, Wireless Embedded Systems, RF Transmission, C programming
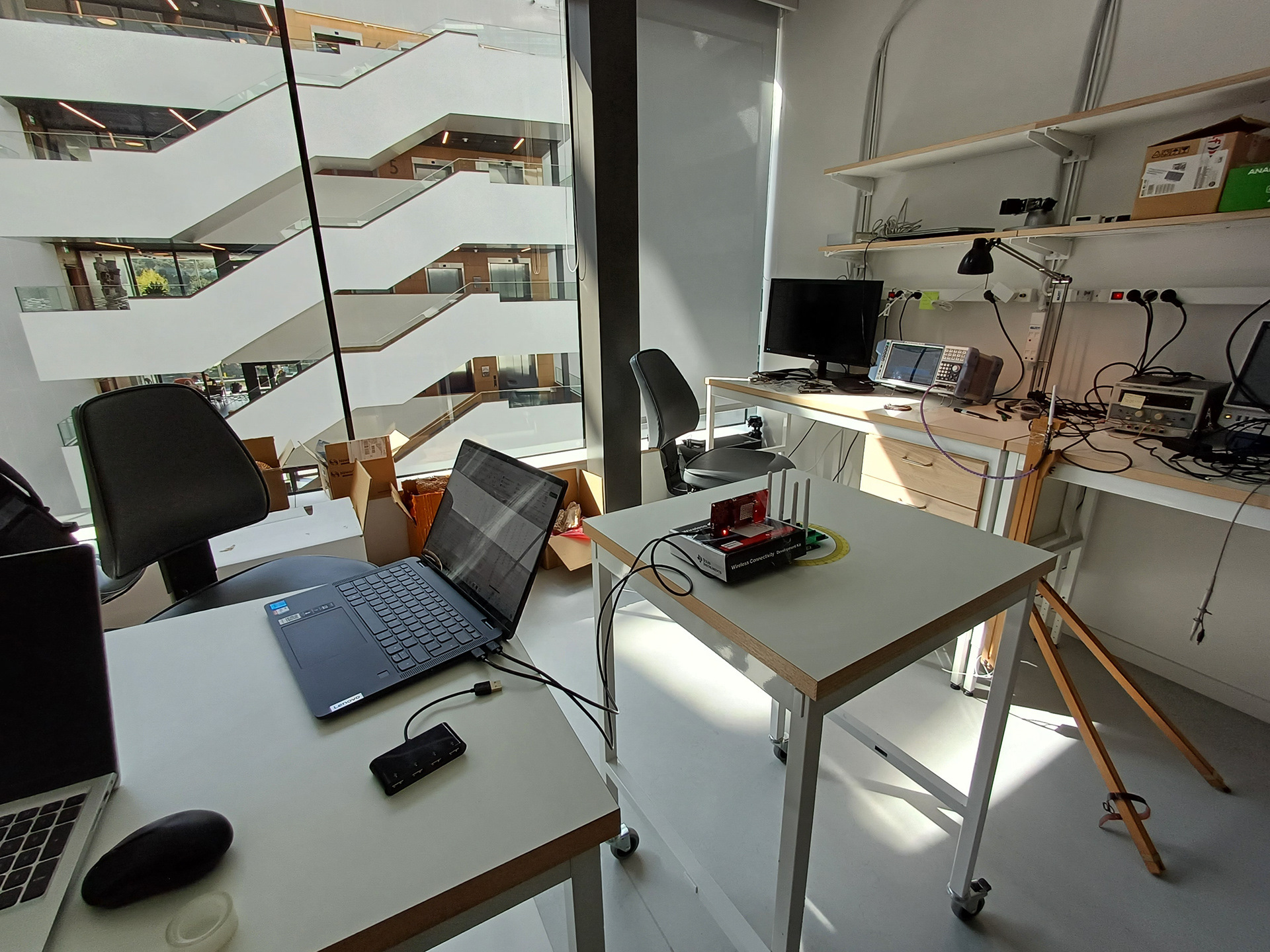



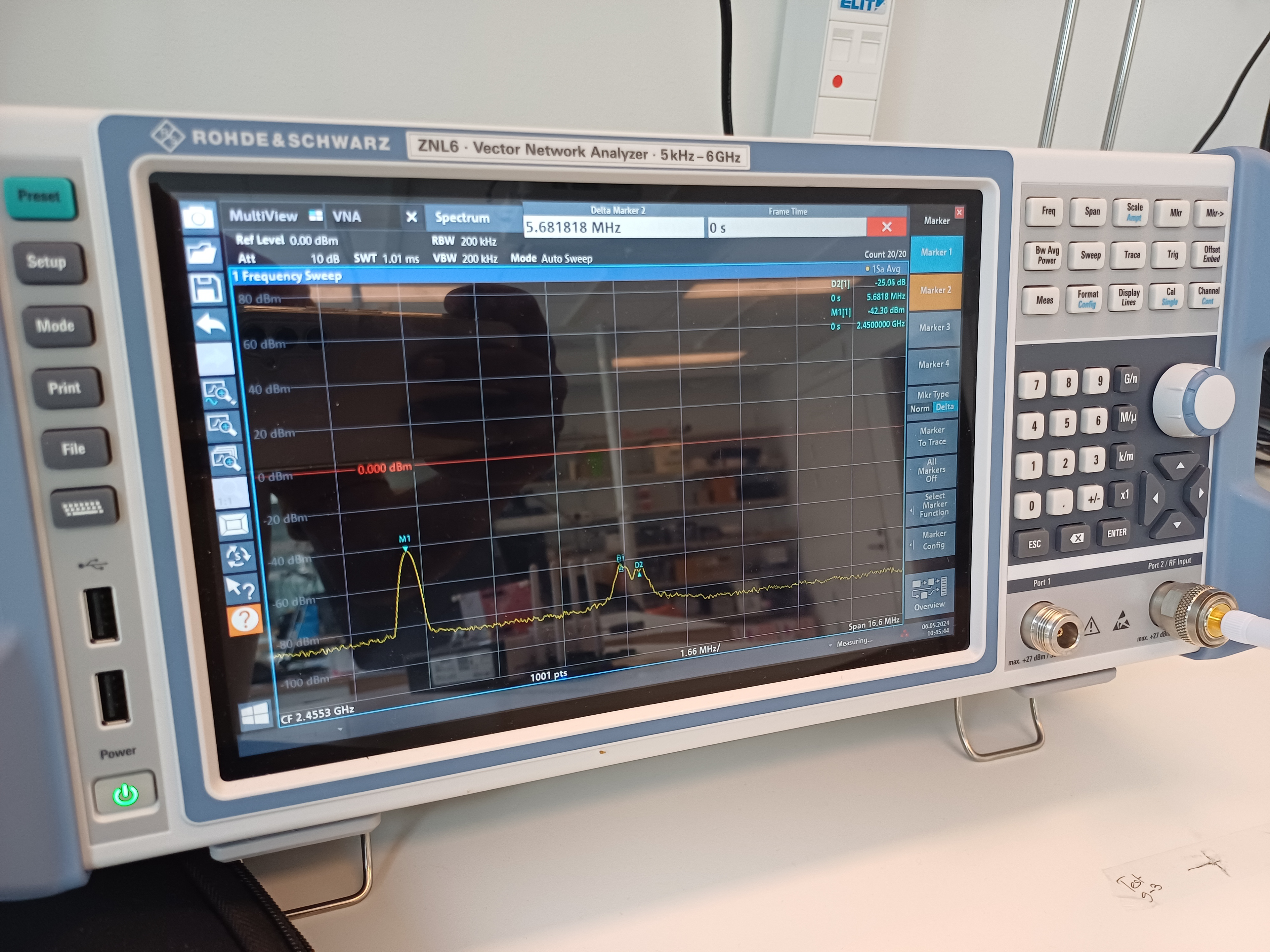
implementation
The setup requires hardware for Carrier, Tag, and Receiver. The Tag frontend was designed by the Research Group of Uppsala University. The processing unit or the backend for the Tag is selected to be the RP2040-Pico development board from Raspberry Pi. The LaunchPad CC1352P7 from Texas Instruments (TI) was used as the receiver and the carrier. The application was developed by using C language.
The Saleae logic analyzer was used to debug GPIO switching, the SmartRF-Studio from TI was used to drive the LaunchPad, and the oscilloscope was used to analyze the impact on signal strength.
results
In our study, we showed that antenna beam steering increases the coverage of Backscatter signals with BFSK modulation. It increases the link budget and improves the communication range without any physical movements of devices
If you are interested in more about our findings, please follow the link here to view the final presentation.